As a manufacturer specializing in high-quality HPMC for the construction industry, I often get asked about the differences between cellulose and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC). With over two decades of experience and an annual output of 10,000 tons, I’ve seen firsthand how understanding these differences can optimize construction projects. Let’s explore the key distinctions to help you choose the right material.

Both cellulose and HPMC are widely used in various industries, but they differ significantly in their structure, solubility, and applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate additive to enhance your construction materials’ performance.
While cellulose serves as a fundamental natural polymer, HPMC is a modified version tailored for enhanced functionality. In our manufacturing process, we leverage HPMC’s unique properties to improve the quality of construction products such as mortars, adhesives, and coatings.
HPMC’s chemical modification enhances its water solubility and film-forming properties, making it ideal for construction applications. True
What Are the Chemical Structure Differences?
The primary difference between cellulose and HPMC lies in their chemical structures. Understanding these structural differences is crucial for selecting the right material for your specific application.
Cellulose is a natural polymer consisting of glucose units, while HPMC is a chemically modified derivative with enhanced solubility and functionality.
- Cellulose: A natural polymer found in plant cell walls, composed of β-D-glucose units linked by β-1,4-glycosidic bonds.
- HPMC: Produced by modifying cellulose, substituting hydroxyl groups with methoxy and hydroxypropyl groups. This modification increases its solubility and flexibility.
HPMC’s modified structure allows it to dissolve in cold water, enhancing its applications in construction materials. True
The chemical modification of HPMC improves its film-forming properties, crucial for coatings and adhesives. True
How Does Solubility Impact Their Usage?
One of the most practical distinctions between cellulose and HPMC is their solubility, which significantly impacts their applications.
Cellulose is inherently insoluble in water, whereas HPMC dissolves readily in cold water to form a gel-like solution.
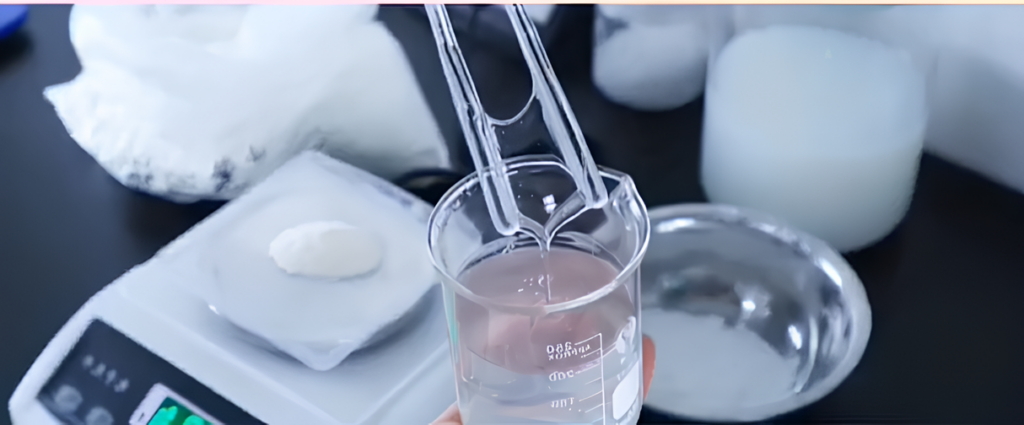

- Cellulose: Requires special treatments to dissolve, limiting its direct use in formulations.
- HPMC: Dissolves quickly in cold water, making it ideal for use in construction applications like tile adhesives and self-leveling compounds.
The superior solubility of HPMC enhances its performance as a thickener and stabilizer in construction materials. True
HPMC’s ability to retain water improves the curing process in cement-based products. True
What Are the Key Physical Properties?
Understanding the physical properties of cellulose and HPMC is essential for optimizing their usage in industrial applications.
While cellulose provides rigidity, HPMC offers enhanced viscosity, flexibility, and film-forming abilities.
| Property | HPMC (Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose) | Cellulose |
|---|---|---|
| Solubility | Highly soluble in cold water, forms a clear, viscous solution | Insoluble in water, requires special treatment to dissolve |
| Viscosity Control | Adjustable viscosity depending on molecular weight and degree of substitution | Fixed viscosity, limited flexibility in adjustment |
| Film-Forming Ability | Excellent film-forming properties, creates smooth, durable films | Limited film-forming capability, often results in uneven surfaces |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Forms gels when heated, retains solubility upon cooling | Less sensitive to temperature, lower stability under heat |
| Thickening Effect | Highly efficient thickener, ideal for construction materials and coatings | Moderate thickening effect, used in low-cost applications |
| Water Retention | Strong water retention, ideal for self-leveling mortars and tile adhesives | Weaker water retention, mainly used for basic thickening purposes |
| Application in Building Materials | Enhances adhesion, water retention, and workability in mortars and plasters | Primarily used in paper, textile, and basic additive applications |
| Environmental & Biocompatibility | Non-toxic, suitable for pharmaceutical and personal care products | Biodegradable but with limited biocompatibility |
- Viscosity: HPMC offers adjustable viscosities, improving the flow and stability of construction mixes.
- Film Formation: HPMC’s film-forming properties make it ideal for coatings and sealants, preventing cracks and enhancing durability.
HPMC’s film-forming ability provides superior surface protection in construction applications. True
The adjustable viscosity of HPMC allows for customized formulations in self-leveling floors. True
Which Industries Benefit Most from HPMC?
HPMC’s versatility has made it a go-to additive across various industries, from construction to pharmaceuticals.
Thanks to its non-toxic and biocompatible properties, HPMC is widely used in construction materials, coatings, and even drug formulations.
- Construction: Enhances the water retention and workability of cement mortars, tile adhesives, and joint fillers.
- Pharmaceuticals: Used in controlled-release drug formulations due to its biocompatibility.
- Paints & Coatings: Provides stability and smooth application in paints, ensuring uniform coverage.
HPMC’s water retention properties extend the open time for cementitious products, enhancing application efficiency. True
In the pharmaceutical industry, HPMC ensures controlled release of active ingredients in drug formulations. True
Conclusion
HPMC stands out as a superior additive due to its enhanced solubility, flexibility, and functionality compared to cellulose. Whether you’re in construction, pharmaceuticals, or coatings, HPMC provides solutions that optimize your products’ performance.
If you’re interested in learning more about how HPMC can improve your project outcomes, don’t hesitate to contact us for tailored recommendations.


